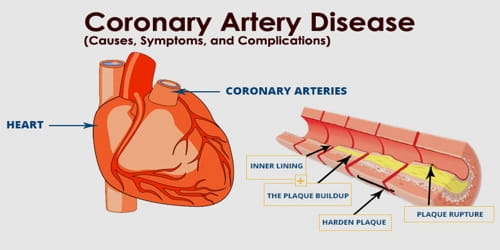
How it happens:
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) is an effect of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), which usually happens when people eat too much of oily and fat-full foods such as bacons, too much that cholesterols starts settling on the heart's major coronary arteries. Your coronary arteries supplies oxygen to your heart muscles with the oxygen full red blood cells. The fats lands into the coronary arteries by diffusing through the artery walls and land on them. Day by day bits fill up and form a plaque. Sometime later, this plaque would be a blockage. When the blood flows too fast, the blood may skim and tear off the top layer of the plaque. Usually in other parts of the body, this is good, but not for the coronary artery. A blood clot would form and block almost the whole of the artery would be blocked and the blood won't be able to past through. The heart muscles would start to starve of oxygen and die. Then, the blood vessels will flow back into the lungs and you will drown yourself.
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) is an effect of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), which usually happens when people eat too much of oily and fat-full foods such as bacons, too much that cholesterols starts settling on the heart's major coronary arteries. Your coronary arteries supplies oxygen to your heart muscles with the oxygen full red blood cells. The fats lands into the coronary arteries by diffusing through the artery walls and land on them. Day by day bits fill up and form a plaque. Sometime later, this plaque would be a blockage. When the blood flows too fast, the blood may skim and tear off the top layer of the plaque. Usually in other parts of the body, this is good, but not for the coronary artery. A blood clot would form and block almost the whole of the artery would be blocked and the blood won't be able to past through. The heart muscles would start to starve of oxygen and die. Then, the blood vessels will flow back into the lungs and you will drown yourself.
Causes:
-Age
-Sex - usually men
-Family
-Smoking
-High blood pressure
-Cholesterol
-Diabetes
-Overweight/Obesity
-Lack of exercise
-Stress
-Unhealthy diet (alcohol, oily foods, sugar)
Symptoms:
-Discomfort
-Fatigue
-Short of breath
-Nausea
-Chest discomfort
 Diagnosis needed:
Diagnosis needed:
-ECG (Electrocardiogram)
-EKG (Echocardiogram
-Stress test/ Exercise tolerant test
-CT (Computed Tomograph)
-MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
-Cardiac Catheterization and Angiogram
-X-Ray
-Blood Test
Risks of Surgery:
-Blood Clots
-Infection
-Over bleeding
-Arrhythmia (Abnormal heart rhythm)
-Pneumonia
-Breathing Problems
-Fever
-Pain
-Kidney Failure
-Memory Loss
-Thought Problems
-Age
-Sex - usually men
-Family
-Smoking
-High blood pressure
-Cholesterol
-Diabetes
-Overweight/Obesity
-Lack of exercise
-Stress
-Unhealthy diet (alcohol, oily foods, sugar)
Symptoms:
-Discomfort
-Fatigue
-Short of breath
-Nausea
-Chest discomfort
 Diagnosis needed:
Diagnosis needed:-ECG (Electrocardiogram)
-EKG (Echocardiogram
-Stress test/ Exercise tolerant test
-CT (Computed Tomograph)
-MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
-Cardiac Catheterization and Angiogram
-X-Ray
-Blood Test
Procedure of surgery
1. Anaesthia
2. Cut open patient’s
chest
3. Open rib
cage
4. Stop heart
for a while
5. Use heart
lung machine to continue pumping blood to the body.
6. Remove
unblocked artery and put on blocked artery.
8. Close the hole
and stitch.
Risks of Surgery:
-Blood Clots
-Infection
-Over bleeding
-Arrhythmia (Abnormal heart rhythm)
-Pneumonia
-Breathing Problems
-Fever
-Pain
-Kidney Failure
-Memory Loss
-Thought Problems