Arthritis:
Arthritis is a medical condition that causes swelling and joint pain and it means any disorder that affects joints. There are more than 100 different kinds of arthritis and the most common are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis usually happens during wear or tear, or some immune system problems.
What is a joint?
A joint is a part of your body which makes the connection between two bones, for instance, the hip bone and the lower leg. An elbow is also a form of joint (hinge joint) which is very complex. These joints are constructed so you can move your bones, your hands and feet.
Symptoms:
-Fatigue
-Joint Swell
-Joint Pain
-Joint Redness
-Joint Warmth
-Joint Tenderness
-Fever
-Anaemia
Causes:
-Injuries (OA ortheoarthritis)
-Abnormal metabolism (MA metabolism arthritis)
-Inheritance (OA...)
-Infections (LA Lyme arthritis)
-Immune systems dysfunctions (RA rheumatoid arthritis/ SLE systemic lupus erythematosus)
What if you don't treat it?
-Destruction/Damage in joint (RA rheumatoid arthritis)
-Ability of moving joint lost
-Bone thinning (Osteoporosis)
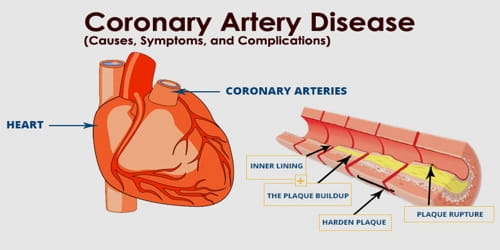
-Coronary Heart/Artery Disease due to inflammation (CHD/CAD) (RA)
-Anaemia (Lack of iron)
-Earlier death
 |
| Joint Fusion |
Treating:
=Surgery=:
-Joint repair - smoothen joint
-Joint replacement - artificial joint
-join fusion - fuse 2 bones into one (usually for smaller bones)
=Ways to kill pain=:
=Therap
-Exercises - flex joints
-Heating packs or ice pads
=Medication=:
-Painkillers
-Counterirritants
-Antirheumatic drugs
-Biological responce modifiers
-Corticosteroids
-Anti-inflammatory drugs